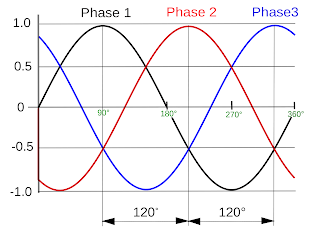
Explanation of roots 3 in the conversion of 3-phase to Single phase - 3-phase voltage is often depicted with 3 pieces of line with one end of the meet, so that each line of an angle 120 degrees. The angle that is called the phase angle difference between the other phase of 120 degrees.
 |
| Explanation of roots 3 in the conversion of 3-phase to Single phase |
 |
| Explanation of roots 3 in the conversion of 3-phase to Single phase |
Figure 1
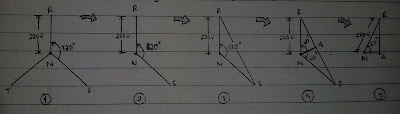
Representation of the 3-phase voltage and neutral, where the phase-to-neutral voltage is 120 volts (VRN = 220V, VSN = 220V, and VTN = 220V).
Figure 2
Footage of two phases, the difference between the two phases is 120 degrees.
Figure 3
a line drawn from R to S, which represents the voltage between phases or VRS.
Figure 4
RSN triangular field, divided in two by drawing the DNA, so that the shape of two triangles which has a shape similar to RNA = SNA angle is equal to 60 degrees.
Figure 5
RNA triangular pieces of figure 4, and from this picture basic calculations begin:
=> Sin 60 = RA/RA
Sin 60 = RA/220
RA = 220 x Sin 60
RA = 220 x 1/2 root 3
RA = 110 x root 3
of the above calculation, return to Figure 4, RS = RA + US, so RS = RA + RA or RS = 2RA, thus:
RS = 2RA RS = 220 x root 3
RS = 2 x (110xroot3) RS = 381,05 = 380 V
0 Response to "EXPLANATION OF ROOTS 3 IN THE CONVERSION OF 3-PHASE TO SINGLE PHASE"
Post a Comment